arrhythmia recognition is a condition characterized by an irregular heartbeat. This can manifest as the heart beating too quickly, too slowly, or in an erratic manner.
Understanding arrhythmia is crucial because it can lead to severe complications if not managed properly. This comprehensive guide explores the various aspects of arrhythmia, including recognition, diagnosis, treatment options, and preventive measures.
Importance of Arrhythmia Recognition
- Early Detection: Timely identification can prevent complications such as stroke, heart failure, and sudden cardiac arrest.
- Personalized Treatment: Helps in tailoring treatments like medication, lifestyle changes, or procedures (e.g., ablation, pacemaker implantation).
- Monitoring: Continuous monitoring can help track the effectiveness of treatments and make necessary adjustments.
arrhythmia recognition: Types and Categories
Atrial Fibrillation (AFib)
Atrial Fibrillation is one of the most common types of arrhythmia, where the heart’s upper chambers beat irregularly.
Supraventricular Tachycardia (SVT)
SVT involves rapid heartbeats originating above the heart’s ventricles.
Ventricular Tachycardia (VT)
VT is a fast heart rhythm that starts in the heart’s lower chambers.
Bradycardia
Bradycardia refers to a slower than normal heart rate.
Premature Contractions
These are early heartbeats originating in the atria (PAC) or ventricles (PVC).
arrhythmia recognition: Symptoms and Signs
Common Symptoms
- Palpitations
- Dizziness
- Shortness of breath
- Chest pain
Uncommon Symptoms
- Fainting
- Fatigue
- Anxiety
arrhythmia recognition: Causes and Risk Factors
Biological Factors
- Heart disease
- High blood pressure
- Diabetes
Environmental Factors
- Stress
- Smoking
- Alcohol consumption
Lifestyle Factors
- Lack of physical activity
- Poor diet
arrhythmia recognition: Diagnosis and Tests
Electrocardiogram (ECG)
An ECG records the electrical activity of the heart and is the primary tool for diagnosing arrhythmia.
Holter Monitor
A portable device worn for 24-48 hours to record heart activity.
Event Monitor
Similar to a Holter monitor but used over a longer period.
Echocardiogram
Uses ultrasound to create images of the heart.
Stress Test
Monitors heart activity during physical exertion.
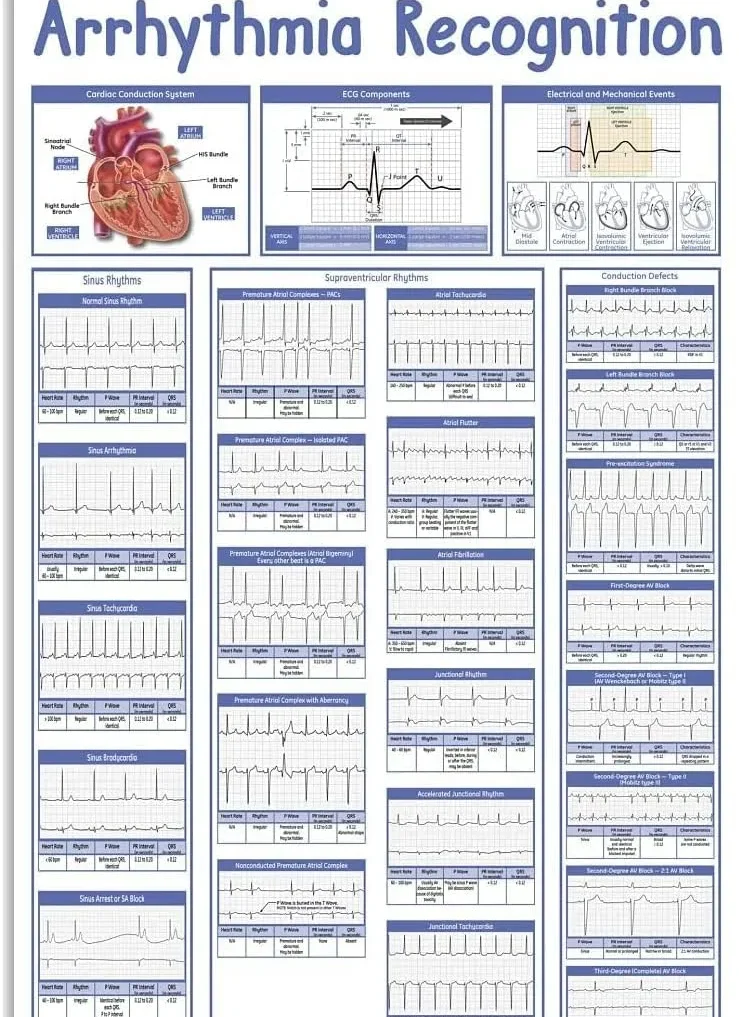
How Do You Recognize Heart Rhythms?
Normal Heart Rhythms
Understanding normal heart rhythms is essential for identifying abnormalities. A normal heart rhythm, known as sinus rhythm, has these characteristics:
- Heart Rate: 60-100 beats per minute.P Wave: Precedes each QRS complex, indicating atrial depolarization.QRS Complex: Represents ventricular depolarization, typically narrow and sharp.T Wave: Follows the QRS complex, indicating ventricular repolarization.
Abnormal Heart Rhythms
Abnormal heart rhythms, or arrhythmias, can be classified based on their origin (atrial or ventricular) and rate (tachycardia or bradycardia):
- Atrial Arrhythmias: Include atrial fibrillation, atrial flutter, and supraventricular tachycardia (SVT).Ventricular Arrhythmias: Include ventricular tachycardia and ventricular fibrillation.Tachycardia: Heart rate over 100 beats per minute.Bradycardia: Heart rate below 60 beats per minute. Using an ECG to Recognize Heart Rhythms
An ECG is pivotal in recognizing heart rhythms. Key ECG findings for normal and abnormal rhythms include:
- Sinus Rhythm: Regular P waves before each QRS complex, consistent intervals.Atrial Fibrillation: Irregularly irregular rhythm with no distinct P waves.Atrial Flutter: “Sawtooth” pattern of flutter waves, usually regular.Ventricular Tachycardia: Wide QRS complexes, rapid rate, no preceding P waves.Ventricular Fibrillation: Chaotic, irregular waveform without identifiable QRS complexes.Bradycardia: Regular rhythm with prolonged intervals between beats.
arrhythmia recognition: Treatment Options
Medications
Antiarrhythmics
Used to restore normal heart rhythm.
Beta-blockers
Reduce the heart rate and improve blood flow.
Calcium Channel Blockers
Help relax the heart muscles.
arrhythmia recognition: Therapies

Cardioversion
A procedure that restores a normal heart rhythm through electrical shocks.
Vagal Maneuvers
Techniques to slow down the heart rate.
Surgery or Other Procedures
Cardiac Catheter Ablation
Destroys areas of heart tissue causing arrhythmia.
Pacemakers
Devices implanted to regulate heartbeats.
Defibrillators
Devices that can send electric shocks to correct arrhythmia.
Clinical Trials
Ongoing research studies exploring new treatments and therapies.
ECG Identification of arrhythmia
Notes on Arrhythmia ECG and Timing
Recognizing the pattern and timing of heartbeats on an ECG.
Determining Regularity of Events on an ECG
Understanding the consistency of the heart’s electrical activity.
Bradycardia or Tachycardia?
Distinguishing between slow and fast heart rates.
Narrow or Broad Ventricular Complexes?
Identifying the width of the QRS complexes on an ECG.
Characteristics of Atrial Tachyarrhythmias
Atrial Flutter
A rapid but regular rhythm.
Broad Complex Tachycardias
Characterized by a wide QRS complex.
Ventricular Tachycardia (VT)
Types of VT, including sustained and non-sustained.
Broad Complex Tachycardias Originating in the Atria
Understanding the source and impact of these arrhythmias.
arrhythmia recognition: Preventive Measures
Lifestyle Adjustments
- Regular exercise
- Healthy diet
- Stress management
Avoiding Triggers
- Limiting caffeine and alcohol
- Smoking cessation
Conclusion
Recognizing arrhythmias and understanding heart rhythms is essential for diagnosing and managing cardiovascular conditions. By interpreting symptoms and utilizing diagnostic tools like ECGs, healthcare providers can identify and treat these potentially life-threatening conditions effectively.
People also ask about arrhythmia recognition
How do you recognize arrhythmias?
Recognizing arrhythmias involves identifying irregularities in the heart’s rhythm. Arrhythmias can be detected through various symptoms, diagnostic tools, and medical examinations.
Common symptoms include palpitations, dizziness, shortness of breath, and chest discomfort. To confirm an arrhythmia, healthcare professionals often use an electrocardiogram (ECG) to monitor the heart’s electrical activity. Additional methods such as Holter monitoring, event recorders, and stress tests may also be employed to identify intermittent arrhythmias.
How do you recognize heart rhythms?
Recognizing heart rhythms involves analyzing the patterns of electrical impulses in the heart. A normal heart rhythm, known as sinus rhythm, is characterized by regular and evenly spaced beats.
Deviations from this pattern may indicate various types of arrhythmias, such as atrial fibrillation, bradycardia, or tachycardia. Healthcare providers use ECGs to visualize these patterns and identify irregularities. The ECG traces the heart’s electrical activity, allowing professionals to observe the rate, rhythm, and electrical conduction. Understanding heart rhythms also requires knowledge of the P wave, QRS complex, and T wave on an ECG.
What are the ECG findings in arrhythmia?
ECG findings in arrhythmia vary depending on the type of irregularity. In atrial fibrillation, the ECG shows an absence of P waves and irregularly irregular QRS complexes.
For ventricular tachycardia, the ECG reveals wide QRS complexes at a rapid rate without preceding P waves. Bradycardia presents with a heart rate below 60 beats per minute, often with a prolonged PR interval. In cases of premature ventricular contractions (PVCs), the ECG displays early QRS complexes that are wide and bizarre in shape. Each type of arrhythmia presents distinct ECG features, aiding in accurate diagnosis and treatment planning.